The female genital anatomy varies widely, and one of the most frequently misunderstood features is the labia minora— the inner folds of skin that surround the vaginal opening. Some women may notice their inner labia to be more prominent or extend beyond the outer labia, raising concerns about normalcy, aesthetics, or comfort. So, what causes labia minora to stick out? The answer lies in a combination of genetics, physiology, hormonal influences, and sometimes pathology.
This article delves into the anatomy, medical science, and clinical conditions that may explain why the labia minora become more pronounced and when, if ever, they warrant medical attention.
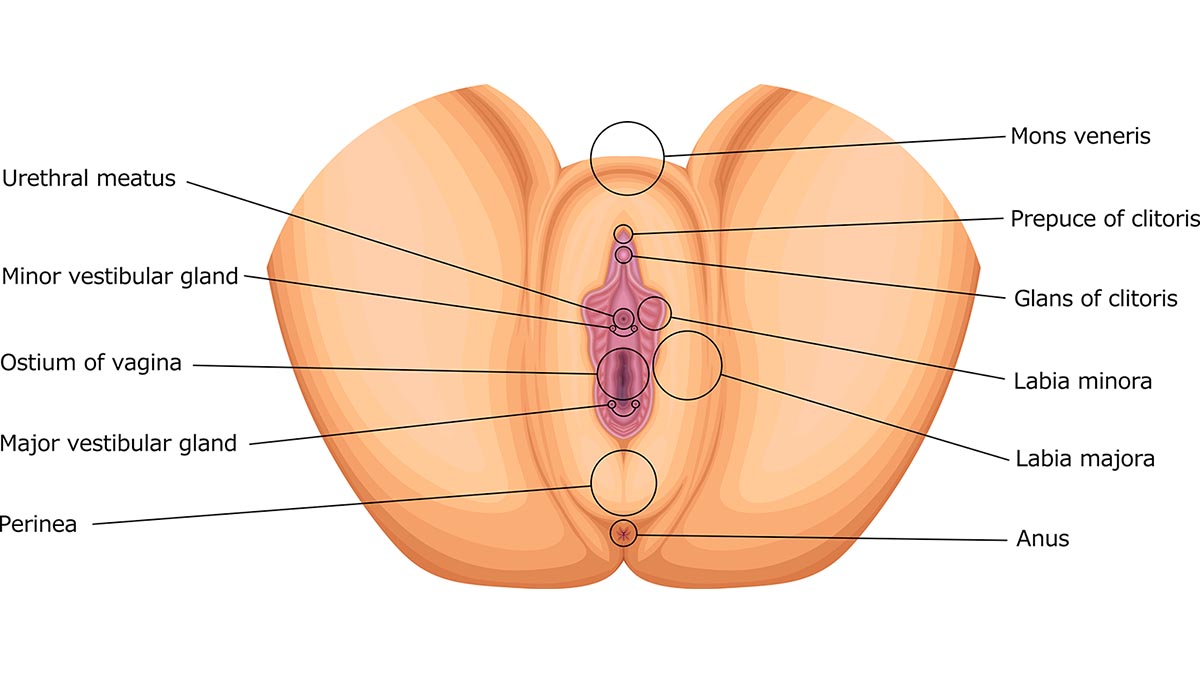
Understanding Vulvar Anatomy: What Is the Labia Minora?
The labia minora are the thin, hairless folds of skin inside the labia majora. Their function is to protect the vaginal and urethral openings, maintain moisture, and contribute to sexual arousal due to their rich nerve supply.

Unlike the outer labia, the inner labia can vary significantly in shape, color, symmetry, and length. For some women, the labia minora naturally protrude several centimeters beyond the labia majora, a variation that is both common and medically normal1.
Causes of Prominent or Protruding Labia Minora

1. Genetic and Developmental Factors
The most common answer to what causes labia minora to stick out is simply genetics. Some women are born with labia minora that are longer, more pigmented, or asymmetrical. This is considered a normal anatomical variant and is not associated with disease.
Hormonal surges during puberty can also stimulate the growth of labial tissue. In fact, adolescent vulvas can change considerably during this time, often leading to the first noticeable development of a saggy labia minora or increased visibility2.
2. Hormonal Influences
Estrogen plays a significant role in vulvar development. During puberty, estrogen causes the labia minora to thicken and elongate. Similarly, pregnancy and hormonal contraceptives can lead to transient changes in the size and elasticity of the inner labia.
Declining estrogen levels during perimenopause may result in loss of elasticity and volume, but paradoxically, some women still report increasingly saggy labia minora, likely due to connective tissue degradation.
Lifestyle and External Factors

3. Physical Activity and Friction
Sports that involve repetitive movement and friction, such as cycling, horseback riding, and running, can place mechanical stress on the labia minora. This may not only elongate the tissue over time but also cause localized inflammation or irritation.
Women often report labia minora itching causes linked to heat, sweat, and friction in these scenarios. In some cases, the tissue may thicken as a protective response, making the labia minora more prominent.
4. Childbirth and Trauma
Vaginal delivery can stretch or tear the labia minora, leading to asymmetry or excess tissue. Episiotomies or natural tears may heal with scarring that alters the natural contour of the labia.
This type of trauma can sometimes result in labia minora hypertrophy, a condition where one or both inner lips grow beyond 4-5 cm in length, often accompanied by discomfort or hygiene challenges3.
Medical Conditions That Can Alter Labial Anatomy

5. Labial Hypertrophy
Labial hypertrophy is a medical term used when the labia minora become significantly enlarged. While not inherently dangerous, it may cause functional issues, such as pain during intercourse, exercise, or even when wearing tight clothing.
Some cases are congenital, while others may be due to hormonal imbalances, chronic inflammation, or mechanical stress. For symptomatic patients, labia reduction or labiaplasty may be considered.
6. Inflammation, Infection, or Cysts
Infections or blocked sebaceous glands can cause a bump on the labia minora or labia minora line, often confused with warts, cysts, or ingrown hairs. Chronic inflammation may also lead to tissue swelling, making the labia minora appear more prominent. Other contributors include:
- Bartholin gland cysts
- Lichen sclerosus
- Contact dermatitis from soaps or hygiene products
These conditions can mimic the appearance of enlarged labia minora or cause swelling, which some mistake for permanent tissue overgrowth.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Most cases of labia minora protrusion are benign and require no treatment. However, seek evaluation if you experience:
- Persistent swelling or signs of infection
- Pain or irritation during intercourse or daily activities
- New growths, such as a bump on the labia minora line
- Unexplained itching, especially chronic or recurrent
Surgical Options: When and Why
Some women pursue surgery not for medical necessity, but for cosmetic or comfort-related reasons. The most common procedure is labiaplasty, which reshapes the labia minora by trimming or removing excess tissue.
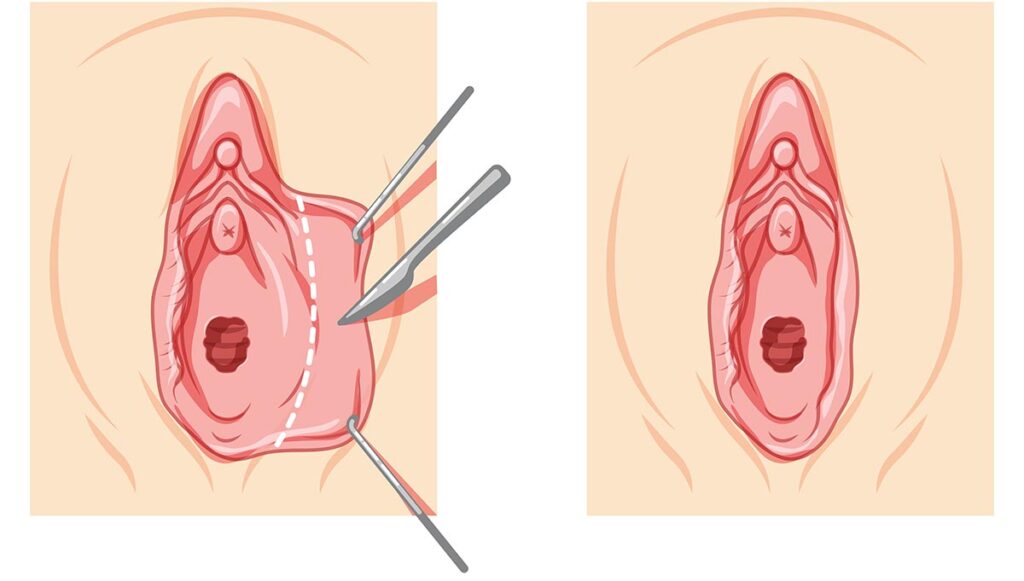
Who May Benefit:
- Those experiencing frequent inner labia chafing or hygiene problems
- Individuals with anxiety or self-consciousness about saggy labia minora
- Women with true labia minora hypertrophy
Recovery:
The typical labiaplasty recovery time ranges from 4 to 6 weeks, with most patients returning to daily activities in about 1 week. Swelling and minor discomfort may persist during the healing process4.
Note: Patients should receive full counselling on risks, expected outcomes, and the natural diversity of vulvar anatomy before opting for labia reduction.
FAQs
How can I flatten my labia?
There is no natural or non-surgical way to “flatten” the labia minora. If physical discomfort or significant asymmetry exists, consult a gynecologist or plastic surgeon to explore surgical options.
Are inner labia supposed to stick out?
Yes, in many cases, what causes labia minora to stick out is simply genetics. This is a normal and healthy anatomical variation.
When to Seek Help for Labia Minora Concerns
Understanding what causes labia minora to stick out requires a balanced view of normal anatomy, hormonal physiology, lifestyle influences, and occasional medical issues. While some women may feel self-conscious or experience physical symptoms, the majority of cases fall within the wide spectrum of natural human variation.

If your concerns are functional or affect your quality of life, consult a healthcare provider for a personalized evaluation. Surgical intervention like labia reduction is an option, but it should be based on well-informed, individual needs rather than societal beauty standards.
At Alinea Labiaplasty & Vaginoplasty NJ, we offer comprehensive vaginal rejuvenation services, including functional and cosmetic procedures tailored to your unique needs. If you are experiencing discomfort, have questions about your anatomy, or want to learn more about treatments like labiaplasty, contact us for a personal consultation.
References
- Lloyd, J., Crouch, N. S., Minto, C. L., Liao, L. M., & Creighton, S. M. (2005). Female genital appearance: “normality” unfolds. BJOG: An International Journal of Obstetrics & Gynaecology, 112(5), 643–646. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-0528.2005.00532.x
- Renaud, M. T., & Moyal-Barracco, M. (2017). Anatomy and embryology of the vulva. In: Bader, R. A., Rose, G. (Eds.). Female Genital Cosmetic Surgery: Solutions for Vaginal Health and Aesthetic Challenges. Springer.
- Goodman, M. P. (2011). Female cosmetic genital surgery. Obstetrics and Gynecology, 117(3), 705–706. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0b013e31820d0c5c
- Sharp, G., Tiggemann, M., & Mattiske, J. (2016). Psychological outcomes of labiaplasty: A prospective study. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, 138(6), 1206–1213. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000002766
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. (2020). ACOG Committee Opinion No. 795: Cosmetic vaginal procedures. https://www.acog.org/clinical/clinical-guidance/committee-opinion/articles/2020/09/cosmetic-vaginal-procedures